CHAPTER 8
Accessing
Organizational
Information – Data Warehouse
History of Data Warehousing
qData warehouses extend the transformation of data into information
qIn the 1990’s executives
became less concerned with the day-to-day business operations and more
concerned with overall business functions
qThe data warehouse provided
the ability to support decision making without disrupting the day-to-day operations
Data Warehouse Fundamentals
qData
warehouse – a logical collection of
information – gathered from many different operational databases – that
supports business analysis activ
ities and decision-making tasks
qThe primary purpose of a data warehouse is to aggregate information
throughout an organization into a single repository for decision-making purposes
qExtraction,
transformation, and loading (ETL) – a process that
extracts information from internal and external databases, transforms the
information using a common set of enterprise definitions, and loads the
information into a data warehouse
qData
mart – contains a subset of data warehouse information
Multidimensional Analysis and
Data
Mining
qDatabases contain information in
a series of two-dimensional tables
qIn a data warehouse and data
mart, information is multidimensional, it contains layers of columns and rows
üDimension – a particular attribute of information
Multidimensional Analysis and Data Mining
qCube – common term for the representation of multidimensional information
qData mining – the process
of analyzing data to extract information not offered by the raw data alone
qTo perform
data mining users need data-mining tools
ØData-mining tool – uses
a variety of techniques to find patterns and relationships in large volumes of
information and infers rules that predict future behavior and guide decision
making
Information Cleansing or
Scrubbing
qAn
organization must maintain high-quality data in the data warehouse
qInformation
cleansing or scrubbing – a
process that weeds out and fixes or discards inconsistent, incorrect, or
incomplete information
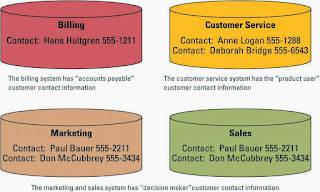
Contact information
in an operational system
qStandardizing Customer name from Operational Systems
qInformation cleansing activities
vBusiness intelligence – information that people use to support their decision-making efforts
v
vPrinciple BI enablers include:
üTechnology
üPeople
üCulture
Technology
vEven the
smallest company with BI software can do sophisticated analyses today that were
unavailable to the largest organizations a generation ago.
vThe largest companies today can create enterprisewide BI systems that compute and monitor
metrics on virtually every variable important for managing the company.
vHow is this possible? The answer is
technology—the most significant enabler of business intelligence.
People
vUnderstanding the role of people in BI
allows organizations to systematically create insight and turn these insights
into actions.
vOrganizations can improve their decision
making by having the right people making the decisions.
vThis usually means a manager who is in
the field and close to the customer rather than an analyst rich in data but
poor in experience.
Culture
vA key
responsibility of executives is to shape and manage corporate culture.
vThe
extent to which the BI attitude flourishes in an organization depends in large
part on the organization’s culture.
Perhaps the most important step an
organization can take to encourage BI is to measure the performance of the
organization against a set of key indicators. 




No comments:
Post a Comment